Leverage allows you to control larger positions with a smaller investment. However, this amplified power comes with a built-in risk management mechanism: the margin call. Simply put, a margin call occurs when your account equity (balance + unrealized profits/losses) falls below a certain threshold relative to the initial margin deposit you placed for your open positions. This threshold is known as the margin maintenance level. When this level is breached, your broker triggers a margin call, essentially a request for additional funds to maintain the minimum margin requirement.
Margin calls play a critical role in safeguarding the forex trading system. Brokers act as intermediaries, facilitating trades between buyers and sellers. If a trader suffers significant losses that wipe out their initial deposit (and potentially dip below zero), the broker can be left holding the bag. Margin calls act as a safety net, ensuring traders have sufficient capital to cover potential losses and maintain the overall financial health of the forex market.
What is a Margin Call in Forex Trading?
A Margin Call is a critical notification from your broker when your account equity dips below the required margin level. This essentially means you need to deposit more funds or close positions to maintain your leverage and avoid potential liquidation. It acts as a safety net for both you and the broker, preventing excessive losses and safeguarding the stability of the market.

The significance of margin calls cannot be overstated. They act as a safeguard for both you and the forex trading system as a whole. By ensuring traders have sufficient capital to cover potential losses, margin calls help to:
- Protect Brokers: Brokers facilitate trades between buyers and sellers. If a trader suffers significant losses and their account balance dips below zero, the broker could be left footing the bill. Margin calls prevent this by ensuring traders have “skin in the game” and can cover potential losses.
- Maintain Market Integrity: Margin calls promote responsible trading behavior and help to maintain the financial health of the forex market. By preventing traders from taking on excessive risk, margin calls contribute to a more stable and secure trading environment.
How does it differ from the Initial Margin Requirement?
While both margin call and initial margin requirement are crucial concepts in forex trading, they serve distinct purposes:
- Initial Margin Requirement: This is the upfront deposit you make to your broker when opening a leveraged position. It represents a percentage (usually between 1% and 5%) of the total position value. Think of it as a down payment on a car – you need to put some money down before controlling a larger asset. The initial margin requirement determines the maximum leverage you can utilize.
- Margin Call: This is a reactive measure triggered by your broker when your account equity (balance + unrealized profits/losses) falls below a certain threshold relative to the initial margin you deposited (known as the margin maintenance level). It’s a safety net to prevent excessive losses. Imagine you miss car payments on your financed car – a margin call would be like the bank contacting you to bring your payments current to avoid repossession (liquidation of your position).
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Initial Margin Requirement | Margin Call |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To control a larger position with a smaller investment | To prevent excessive losses and maintain leverage |
| Timing | Paid upfront when opening a position | Triggered when account equity falls below a threshold |
| Amount | Percentage of total position value (e.g., 2%) | Varies depending on account equity decline |
| Action by Trader | Deposit initial margin to open position | Deposit additional funds or close positions |
| Consequence of Not Meeting | Limits maximum leverage | Potential forced liquidation of positions |
What triggers a Margin Call in Forex Trading?
Imagine you’re driving a car financed with a loan. You make monthly payments to cover the cost of the car. In forex trading, leverage acts like a loan, allowing you to control a larger position with a smaller investment. However, just like with a car loan, there’s a minimum amount you need to maintain in your account to keep your position open – this is where margin calls come in.
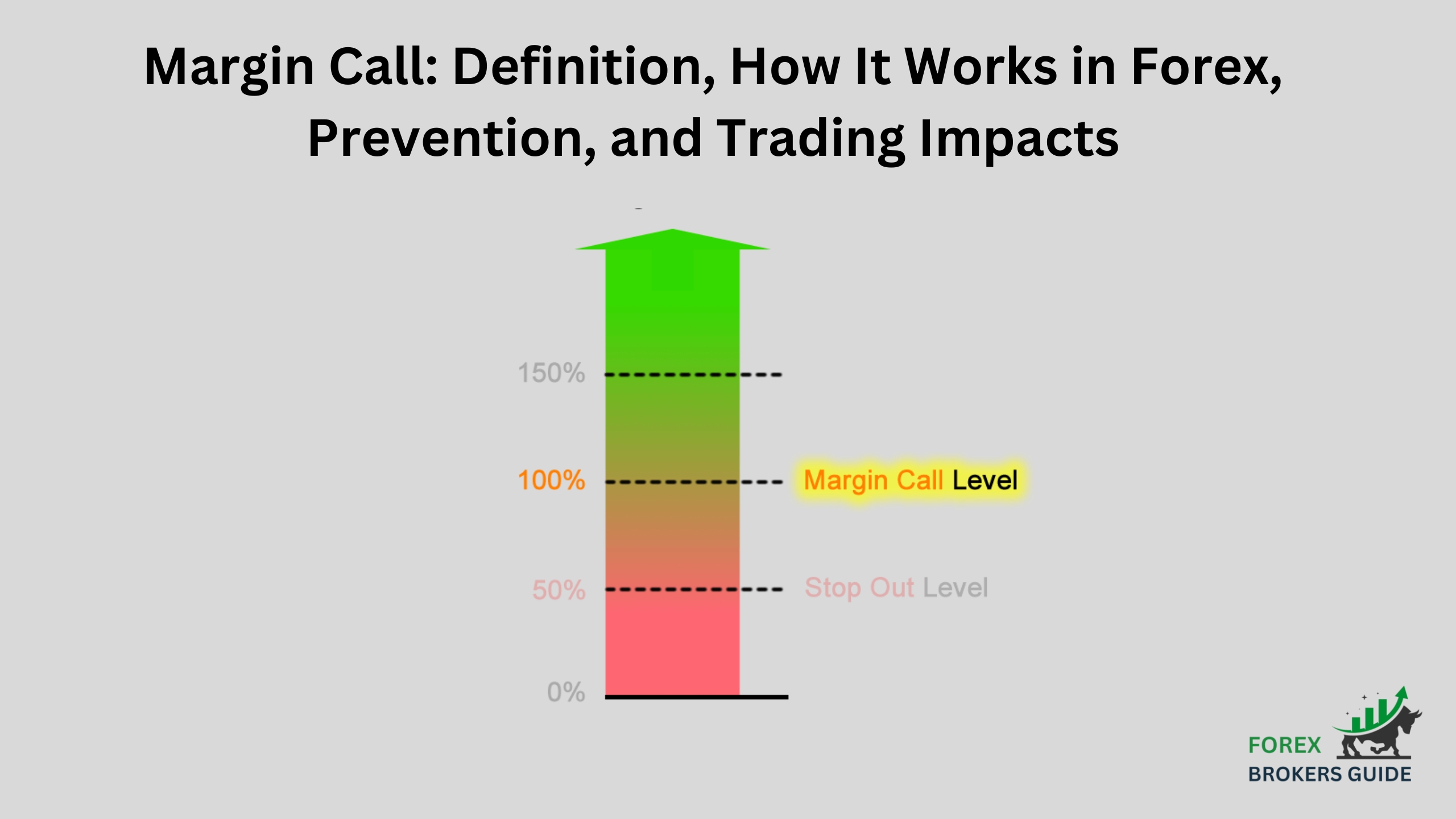
A margin call is triggered when your account equity, which is your current account balance plus any unrealized profits or losses, falls below a specific threshold relative to the initial margin you deposited. This threshold is known as the margin maintenance level. It’s a percentage set by your broker, typically ranging from 50% to 80% of the initial margin requirement.
Here’s a breakdown of what triggers a margin call:
- Market Moves Against Your Position: If the market moves against your open positions, the value of your position decreases, leading to unrealized losses.
- Account Equity Decline: As unrealized losses accumulate, your account equity (balance + unrealized profits/losses) starts to decline.
- Breaching the Margin Maintenance Level: When your account equity falls below the margin maintenance level (a percentage of the initial margin), your broker triggers a margin call.
How do adverse Market Movements Affect Margin Levels?
Adverse market movements, where prices move against your open positions in forex trading, can have a ripple effect on your margin levels. Here’s how it unfolds:
Imagine you enter a trade expecting the Euro (EUR) to strengthen against the US Dollar (USD). However, the market moves against you, and the EUR weakens. This decline in the Euro’s value translates to unrealized losses in your position. These unrealized losses directly eat into your account equity, which is your current account balance plus any unrealized profits or losses.
As these unrealized losses accumulate, your account equity starts to shrink. Remember, for your positions to remain open, your account equity needs to stay above a specific threshold relative to your initial margin deposit. This threshold is known as the margin maintenance level.
With a declining account equity, the gap between your current standing and the critical margin maintenance level starts to shrink. This puts pressure on your margin level, squeezing it tighter. The more your positions lose value due to adverse market movements, the more this gap narrows.
If the market continues to move against you and your account equity dips below the margin maintenance level, a critical event occurs: a margin call. This serves as a warning from your broker, informing you that you need to take immediate action. You’ll either need to deposit additional funds to increase your account equity or close some of your open positions to reduce the margin requirement. If you fail to respond to a margin call, your broker may be forced to liquidate your positions at unfavorable market prices to recover their loaned funds, potentially leading to even greater losses.
What are the Consequences of Receiving a Margin Call?
A margin call in forex trading might seem like a minor inconvenience at first, but it can have significant consequences for your trading experience and financial well-being. Here’s a closer look at the potential repercussions:
- Forced Liquidation: The most severe consequence of ignoring a margin call is forced liquidation. If you fail to respond by depositing additional funds or closing positions to meet the margin requirement, your broker may be forced to close your open positions at the prevailing market price. This price might not be ideal, potentially leading to substantial losses exceeding your initial investment.
- Loss of Capital: Margin calls can quickly erode your trading capital, especially if you’re using high leverage and experiencing significant losses. The forced liquidation at potentially unfavorable prices can wipe out a large chunk of your initial deposit, hindering your ability to continue trading.
- Psychological Impact: Margin calls can be stressful and damage your trading confidence. The fear of receiving another call can lead to impulsive decisions to avoid them, potentially worsening the situation. This can create a cycle of anxiety and fear, hindering your ability to make sound trading judgments.
- Damaged Trading Reputation: Depending on your broker’s policies, repeated margin calls could negatively impact your trading reputation. Some brokers might restrict your account or even close it entirely if you experience frequent margin calls.
How can a Margin Call force a Trader to Close Positions?
A margin call in forex trading acts like a red flag, a warning that your account equity (balance + unrealized profits/losses) has dipped below the critical margin maintenance level set by your broker. This situation can force you to close some or all of your open positions, and here’s how it unfolds:
Imagine you open a leveraged position to buy EUR/USD, expecting the Euro to appreciate. However, the market moves against you, and the Euro weakens. This decline translates to unrealized losses in your position, eroding your account equity.
As losses accumulate, your account equity shrinks, and the gap between your current standing and the crucial margin maintenance level starts to narrow. If this gap closes entirely, triggering a margin call, you’ll be presented with two unappealing options:
- Deposit Additional Funds: The most straightforward solution is to add more money to your account. This increases your account equity and brings it back above the margin maintenance level, effectively silencing the margin call. However, this requires readily available capital, which may not always be the case.
- Close Open Positions: If depositing additional funds isn’t an option, you’ll be forced to close some or all of your open positions to reduce the overall margin requirement. This essentially means selling your currency holdings at the current market price, even if it’s unfavorable.
The forced closure can have significant drawbacks:
- Unfavorable Price: Market conditions that trigger a margin call often involve adverse price movements. Being forced to close positions at this time might lock in substantial losses, potentially exceeding your initial investment.
- Loss of Potential Gains: If the market eventually reverses direction and your original trade call becomes profitable, you’ll miss out on those potential gains because you were forced to close your positions prematurely.
- Limited Trading Options: Having to close positions due to a margin call reduces your available capital and limits your ability to participate in the market until you replenish your account.
What are the Potential Financial Repercussions of a Margin Call?
A margin call in forex trading might seem like a temporary hiccup, but it can leave a lasting financial sting. Here’s a closer look at the potential repercussions that can impact your wallet:
- Amplified Losses: The most immediate financial consequence of a margin call is the potential for magnified losses. If you’re forced to liquidate positions at an unfavorable market price to meet the margin call, you could lose a significant portion of your initial investment, and potentially even more. Remember, leverage cuts both ways – it magnifies not only profits but also losses. A margin call can trigger a domino effect, where unrealized losses quickly snowball into substantial real losses due to forced liquidation.
- Account Depletion: Margin calls can rapidly deplete your trading capital, especially if you’re using high leverage and experience significant losses. The forced liquidation at potentially unfavorable prices can wipe out a large chunk of your initial deposit, hindering your ability to continue trading or recover from the losses. This can be particularly detrimental for beginner traders who may not have a large pool of capital to start with.
- Limited Trading Opportunities: A margin call and subsequent liquidation can significantly reduce your available capital. This limitation can restrict your ability to participate in the forex market until you replenish your account. The time and effort required to rebuild your capital can be discouraging and hinder your overall trading progress.
- Debt Potential: In some cases, depending on your broker’s policies and the leverage ratio used, a margin call could lead to a negative account balance. This essentially means you owe your broker money to cover the shortfall created by the liquidation. This debt can accrue interest charges and put additional financial strain on your situation.
How can Forex Traders Avoid Margin Calls?
The ever-present threat of a margin call can be nerve-wracking for forex traders. However, by adopting a proactive approach and employing sound risk management strategies, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering one. Here are some key tactics to keep those margin calls at bay:
1. Leverage Wisely:
Leverage, while a powerful tool, can be a double-edged sword. Avoid the allure of extremely high leverage ratios, especially if you’re a beginner. Start with lower leverage ratios (e.g., 10:1 or 20:1) to gain experience and manage risk effectively. As your experience and risk tolerance grow, you can gradually increase leverage if necessary.
2. Embrace Stop-Loss Orders:
Stop-loss orders act as your automated risk management allies. These pre-defined orders automatically exit your positions when the market reaches a specific price level, limiting potential losses. By setting stop-loss orders strategically, you can prevent unrealized losses from spiraling out of control and triggering a margin call.
3. Maintain a Healthy Margin Level:
Don’t let your account equity get precariously close to the margin maintenance level set by your broker. Regularly monitor your account and maintain a buffer between your account equity and the threshold. This buffer zone provides breathing room for market fluctuations without triggering a margin call. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a margin level well above the maintenance level (e.g., 100% or even 150%).
4. Manage Your Position Sizing:
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Distribute your trading capital across multiple positions, limiting the risk exposure on any single trade. This approach prevents a single adverse market movement from wiping out a significant portion of your account equity and pushing you closer to a margin call.
5. Develop a Trading Plan and Stick to It:
Having a well-defined trading plan that outlines your entry and exit strategies, risk management parameters, and capital allocation helps maintain discipline and prevents impulsive decisions fueled by emotions. Sticking to your plan during market volatility can prevent you from taking excessive risks that could lead to a margin call.
6. Practice Good Money Management:
Forex trading requires responsible financial management. Only risk capital you can afford to lose. Don’t chase losses or trade with borrowed money. Remember, consistent and sustainable profits come from sound risk management, not reckless gambling.
How can Monitoring Account Equity and using Stop-loss Orders help mitigate Risk?
Forex trading offers the potential for significant rewards, but it also carries inherent risks. By understanding the concept of margin calls and the potential consequences, you can approach the market with a healthy dose of caution. Employing responsible risk management strategies, such as monitoring account equity diligently, using stop-loss orders effectively, and maintaining a healthy margin level, is paramount for navigating the forex market successfully. Remember, consistent and sustainable profits stem from calculated risks and a focus on risk mitigation, not reckless gambling. With a well-defined trading plan, sound risk management practices, and a disciplined approach, you can transform the potential pitfalls of margin calls into stepping stones on your path to forex trading success.
